IT service providers need to offer services that deliver value to their customers whilst increasing levels of availability, controlling risks and reducing costs. Organisations also need to manage transformation and rapid change as there are often mergers, acquisitions, legislation, sourcing decisions, competition, technology innovations and changes in customer needs.
Many organisations have demonstrated that implementing a service management system required by ISO/IEC 20000 with repeatable and auditable processes improves a service provider's ability to address these challenges. The number of organisations that have adopted ITIL® and achieved ISO/IEC 20000 certification has been growing rapidly across the world and this trend will increase significantly in 2008.
Adopting ITIL® V3® principles and practices can help organisations that are aiming to achieve ISO/IEC 20000 certification.
ISO/IEC 20000 and ITIL®
ISO/IEC 20000 is the IT service management auditing standard that is aligned with ITIL®. The Office of Government Commerce (OGC), the owner of ITIL®, has always been committed to maintaining an alignment between ITIL® and the IT service management standard. ITIL® Version 2 was developed in alignment with BS 15000, the former UK standard for IT service management. The ITIL® V3 publications are centrally co-ordinated by The Stationery Office (TSO) and the official accreditation body, for the ITIL® v3 qualification scheme is the APMG.
The new version of ITIL® V3, released in June 2007, provides further guidance to organisations that are aiming to achieve ISO/IEC 20000 certification. It comprises a set of core texts supported by additional complementary and web-based materials. Some of the key success factors for ITIL® Version 3 were to build on the ITI® V2 and support easier integration of ITIL® with ISO/IEC 20000. Applying ITIL® V3 principles and practices can help organisations to achieve the requirements specified in ISO/IEC 20000. The role of ITIL® is shown in Figure 1.
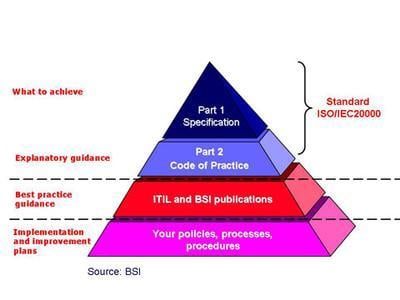 Figure 1. How ITIL® supports ISO/IEC 20000
Figure 1. How ITIL® supports ISO/IEC 20000
Delivering what the customer needs
ISO/IEC 20000 requires a service provider to deliver managed services of an acceptable quality for its customers. To do this an organisation must:
- understand and measure how it provides services that add value to its customers;
- provide real value to the business by designing, developing and improving the IT services with the business objectives in mind.
ITIL® V3 provides concepts, models and guidance on integrating all aspects of IT service provision to deliver value to the business and customers. These models enable an IT service provider to understand and measure complex services across the supply chain.
The service management system
ISO/IEC 20000 is a management system standard, similar to the quality management system ISO 9000 family of standards and the information security standard, ISO/IEC 270001. An objective of ISO/IEC 20000 is to provide a service management system, including policies and a framework to enable the effective management and implementation of all IT services to meet the business requirements.
The architecture of the ITIL® V3® core library combines the process based view of ITIL® with a service life cycle approach, shown in Figure 2. This strongly supports organisations where the management systems, roles, and responsibilities require the use of multiple control perspectives that include:
- The objectives for those responsible for the design, development and improvement of service management processes are best achieved using a process view of the organisation.
- The objectives for those responsible for the design, transition, operation, and improvement of services and contracts using a lifecycle view.
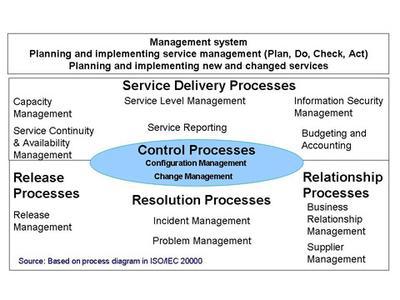 Figure 2. ITIL® V3 service life cycle
Figure 2. ITIL® V3 service life cycle
ITIL® V3 covers development of a strategy for the service management system, how this is then designed and transitioned into service operation and continually improved.
ISO/IEC 20000 requires that 'All service management roles and responsibilities shall be defined and maintained together with the competencies required to execute them effectively.' Internal training can be supplemented by formal professional qualifications to achieve this requirement. The ITIL® V3 qualification scheme will provide more flexibility and choice for service management professionals as they develop their career.
How ITIL® V3 supports the planning and implementation of service management
ISO/IEC 20000 specifies a number of closely related service management processes, as shown in Figure 3. These processes are all supported by the processes and practices in ITIL® V3. The standard recognises that the relationships between the processes depend on the application within an organisation and that these are complex to model. ITIL® V3 provides guidance on managing the complexity related to integrating the processes, changing services and the service management processes.
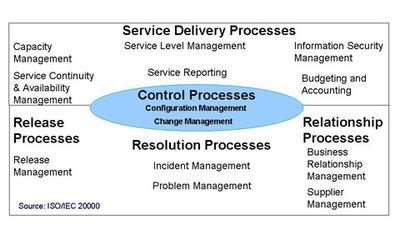 Figure 3. ISO/IEC 20000 service management framework of processes
Figure 3. ISO/IEC 20000 service management framework of processes
The guidance on planning and implementing the service strategy covers the principles underpinning the practice of service management. These principles are useful for developing the service management processes required for achieving ISO/IEC 20000 certification. Adopting these principles helps a service provider to demonstrate that the delivery of its managed services meets the business and customer requirements effectively.
ISO/IEC 20000 recognises that adopting a coordinated and integrated implementation of the service management processes delivers the ongoing control, greater efficiency and opportunities for continual improvement.
Consistent with the structures adopted by high-performing businesses today and standards bodies around the world, the ITIL® service life cycle approach embraces and enhances the interpretation of the Deming quality cycle of plan, do, check, act. This quality cycle is used in the structure of the practices in each of the core guides.
The ITIL® V3 service management practices provide guidance on:
- establishing the integration of business strategy with IT service strategy;
- establishing the service management systems, policies, guidelines, and processes across the ITIL® service life cycle;
- ensuring that the organisation can handle the costs and risks associated with their service portfolios;
- developing a knowledge capability for decision and management of services;
- measuring and demonstrating value delivered to the customer's business.
The ITIL® V3 service strategy publication covers:
- service management strategy and value planning, linking IT service strategy to business needs;
- service economics;
- planning and implementing service strategy.
The ITIL® V3 continual service improvement core publication covers the identification and triggers for improvement and change anywhere in the service life cycle. It uses a closed-loop feedback system, based on the plan, do, check, act (PDCA) cycle required by ISO/IEC 20000. It covers the ways that the overall process and service provision can be improved.
ISO/IEC 20000 - planning and implementing new and changed services
Many organisations that have a dynamic, high-risk, rapidly changing business environment continually introduce new services and change existing services. For example, in order to increase or maintain value to customers over the life cycle of services, achieve service levels, and conform to standards and regulations.
The ITIL® V3 service life cycle approach supports the ISO 20000 requirements for planning and implementing new and changed services. The ITIL® V3 guidance includes the following service life cycle stages:
Service design
This stage turns the service strategy into the blueprint for delivering the business objectives. It provides guidance on developing a solution designed to meet the current and future business requirements. It also covers the development of IT policies, architectures, and documents required to design the appropriate IT services solutions and processes.
Service transition
This provides guidance for the development and improvement of capabilities for transitioning new and changed services into a live service operation. It provides guidance on how the requirements of service strategy encoded in service design are effectively realised in service operation while controlling the risks of failure and disruption.
Service operation
This covers the business as usual activities and functions that operate the services and infrastructure, including the service desk, IT operations management, technical management and application management. It includes the practices for operations, management, control and measurement.
Summary
Figure 4 shows a high-level summary of how ITIL® V3 guidance will support an organisation that is trying to achieve the ISO/IEC 20000 requirements. As discussed earlier, many sections of the standard are covered across the ITIL® V3 publications. The scope of the specific service management processes in relation to the service life cycle is shown in the diagram.
For example, service level management is covered in the service design book but any significant changes to the service level management process and supporting systems will go through the service life cycle i.e. from service design through service transition and into service operation. Service strategy and continual service improvement provide the service life cycle governance processes.
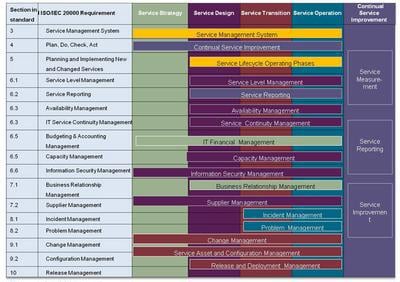 Figure 4. High-level view of how ITIL® V3 supports the ISO/IEC 20000 requirements
Figure 4. High-level view of how ITIL® V3 supports the ISO/IEC 20000 requirements
The OGC and TSO are planning to publish an official mapping of ITIL® V3 and ISO/IEC 20000 as part of the additional complementary and web based materials.
ITIL® is a registered trade mark, and a registered community trade mark of the Office of Government Commerce, and is registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.